Indeed, even the most natural gardener isn't a fan of bugs that wreak havoc on a raised bed loaded with plants and vegetables. Fortunately, you can keep away these unwelcome guests with straightforward, non-toxic techniques. Pesticides, which can affect the insects you actually want around your plants along with other creatures, ought to be utilized only if all else fails.
Along with irritating insects, there are several other larger pests that can destroy a flower garden or eat up your best vegetables if they are not controlled. In the following paragraphs you will learn about some of the most common backyard pests, that not only effect plants but can also be bothersome to the people trying to enjoy the backyard. You’ll also see tips on how to get rid of them most effectively.
Aphids
How to recognize them
These tiny, green, pear-shaped bugs have long tentacles and two tubes starting from the back of their midriff. They, for the most part, hang out on most products of the soil, like blossoms, ornamentals, and shade trees all through North America.

What damage do they do?
Aphids suck plant sap, making foliage twist and leaves to drop; honeydew discharged on leaves bolsters dirty shape development; and sustaining spreads viral infections.
How to get rid of them?
To control these bugs, wash plants with a solid splash of water; empower local predators and parasites, for example, aphid midges, lacewings, and woman bugs; when practical, cover plants with drifting line cover; apply hot-pepper or garlic repellent showers; or for serious issues, apply green oil, insecticidal cleanser, or neem.
Potato Beetle
How to identify them
Grown-ups are yellow-orange insects with ten dark stripes on wing covers. They can be found on vegetables and fruits like potatoes, cherry tomatoes, eggplant, tomatoes and petunias all through North America.

The damage they cause
These scarabs defoliate plants, diminishing yields or murdering young plants.
How to get rid of them?
To control, apply thin line covers; utilize profound straw mulches; hand pick; pull in local parasites and predators; splash with neem oil.
Earwigs
How do I recognize them?
These thin, crimson creepy crawlies (3/4 inch long) with prolonged bodies are recognized by a couple of sharp pliers at the rear, which they use for catching prey and mating. A couple of animal varieties have wings, in spite of the fact that it is not a solid flier, and generally creeps looking for food. Earwigs get their name from an old superstition that they creep into the ears of a dozing individual and drill into the cerebrum. While threatening in appearance, they are safe to humans.

What damage do they do?
Basically night feeders, the regular earwig (Forficula auricularia) is thought to be a creepy crawly bother when it nourishes on delicate plant shoots, for example, corn silks, and eats little gaps in foliage and blooms. Some of the old natural products are invaded, yet harm is generally mediocre. It can be especially harming to seedlings.
How do I get rid of them?
On the off chance that earwigs end up plainly pestiferous there are a few successful natural techniques that can be utilized for disposing of them.
- Throw cultivated garbage and over the top mulch where earwigs are living and reproducing.
- Since earwigs rarely fly, a sticky band of Tanglefoot Pest Barrier around the trunks of trees, bushes, and woody plants will keep them from approaching the leaves and natural products on which they feed.
- Use Insect Killer Granules around establishments, gardens and scenes to dispense with or repulse a wide range of troublesome nuisances.
- Apply sustenance review Diatomaceous Earth for dependable insurance. Comprised of minor fossilized sea-creatures, it looks like broken glass under the magnifying instrument, DE works by scoring a bug's external layer as it slithers over the fine powder. Contains NO lethal toxins!
- Disseminate Monterey Ant Control, a sheltered and natural snare containing iron phosphate and spinosad, uniformly over the dirt around or close regions to be ensured.
- Minimum lethal organic bug sprays ought to be utilized if all else fails. Obtained from plants which have insecticidal properties, these normal pesticides have less destructive symptoms than manufactured chemicals and operate all the more rapidly in the soil.
Grasshoppers
How does one recognize them?
Grown-ups (1-2 inch long) are dark, to rosy-yellow, or green in color with unmistakable jaws, completely formed wings and short reception apparatuses. They have developed rear legs and can bounce extraordinary separations. Juvenile stages — sprites — are more distinctive in appearance than grown-ups, yet are smaller and have wing buds rather than wings.
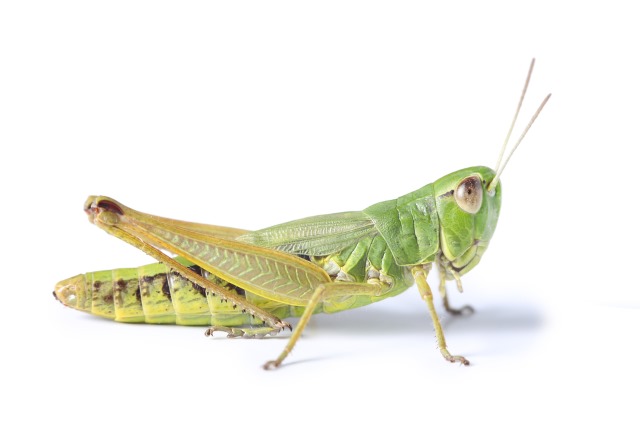

What damage do they do?
Grasshoppers are insatiable feeders, devouring around one-portion of their body weight every day. Both grown-ups and young ones cause harm by biting on the leaves and stems of plants, and if invasions are extreme, may defoliate whole fields. It is assessed that grasshoppers expend up to 25 percent of the accessible rummage in the western United States yearly.
How to get rid of them?
- Roto-till in the spring to destroy overwintering eggs.
- Reap Guard push spreads can be utilized to cover and secure smaller garden regions.
- For long-time grasshopper insurance, apply natural Semaspore Bait (Nosema locustae) to bring forth beds – field edges and other undisturbed lush regions – when grasshoppers are young. Substantial invasions may require various applications.
- Azamax contains azadirachtin, the key insecticidal ingredient found in neem oil. This concentrated spray is endorsed for natural utilization and offers different methods of activity, making it, for all intents and purposes, outlandish for nuisance imperviousness. The best part is that it's non-poisonous to bumble bees and numerous other helpful creepy crawlies.
- Spread EcoBran Bait or apply herbal bug sprays, for example, natural pyrethrins, to areas where you are encountering overwhelming grasshopper damages and require a speedy execution.
Slugs and Snails
How to recognize them
Snails/Slugs are not genuine bugs, but instead individuals from the mollusk phylum. Therefore, they are firmly identified with snails in structure and science, aside from that; snail has a shell which the slug does not. Both garden bugs depend on their strong foot to both move and discharge mucous, or ooze on where they coast. This sparkly ooze trail frequently gives them away as it denotes their travel. They flourish in soggy, shady spots and can frequently be found along establishments, under rocks or in all around mulched cultivated regions.


What damage they do
Most dynamic around evening time, they feast upon an assortment of living plants and also on rotting plant material. Both bite substantial gaps in foliage and may do major harm to seedlings, delicate, low-developing, verdant vegetables and maturing natural product, for example, strawberries, artichokes and tomatoes. All garden vegetables, fancy blossoms, and some trees, particularly citrus are liable to assault.
How to get rid of them
- Handpicking bugs can make a sizable dent in their density, and is most profitable at night, two hours after dusk.
- In the case of handpicking is badly arranged, take a stab at catching. Portions of cardboard, cabbage leaves, rocks or plywood all make phenomenal traps for daytime gathering.
- Shallow dish of stale lager sunk into the dirt can likewise be utilized. The yeast in the brew draws in these pests, which fall in and suffocate. For best outcomes, plant lager every couple of days or after a rain.
- Copper Tape and diatomaceous earth are well known boundaries that keep pests from eating the leaves, or products of the soil on which they encourage.
- Bring in climate safe boric corrosive granules around blossom gardens, ground spreads and ornamentals to dispense with slugs and snails. Re-apply like clockwork, as required.
- Sluggo is a natural lure, containing iron phosphate, which can be scattered on the grass or on the dirt around any vegetables, blooms, organic product trees or shrubs to diminish bug numbers.
Flies
How does one identify them?
House fly grown-ups (1/6 – 1/4 inch long) are dull in color with rosy, dark eyes. They have two membranous wings and four dim stripes down the center of their body (thorax). Females are normally bigger than males and can be recognized by the space between their eyes, which is double the separation as in guys. The larval stage (3/8 – 3/4 inch), otherwise called a hatchling, is delicate, cream-shaded and worm-like. They are regularly found around spoiling natural matter, for example, fertilizer heaps or rubbish jars, and are fairly carrot formed.

What damage do they do?
It has been related with more than 100 distinctive infection pathogens, including salmonella, cholera and tuberculosis, so it is essential to oversee bug episodes. When nourishing, flies spew fluid from the stomach to break up food, at that point utilize their wiping mouthparts to suck it up. They leave fecal spots, or “bits”, where they have strolled, and along these lines may give sickness to people and other creatures. In provincial regions, flies can be a disturbance when they assemble on the outside dividers of homes and structures on summer nights.
How to get rid of them?
- Sanitation is the best and imperative stride in diminishing nuisance numbers. Dry and wrap natural waste before setting it in the trash can. Seal trash jars with tight fitting tops.
- Screen windows and ways to let flies remain out. Utilize indoor traps or sticky tape to oversee them inside the house.
- Hang sticky, non-pesticide traps outside close territories — horse shelters, pet hotels, waste receptacles — to catch flies by the thousands.
- Minimally lethal natural bug sprays ought to be utilized if all else fails. Gotten from plants which have insecticidal properties, these characteristic pesticides have less destructive reactions than manufactured chemicals and separate all the more rapidly in nature.
Moles
How does one recognize them?
Moles are a little (7 inches long, including tail), typically dim or dark colored warm blooded creatures, that can be recognized from glade voles, gophers, and wenches by their stripped, pointed nose. They have little eyes and ears, which are covered by hide and huge spade-like front feet that work well for them for burrowing.
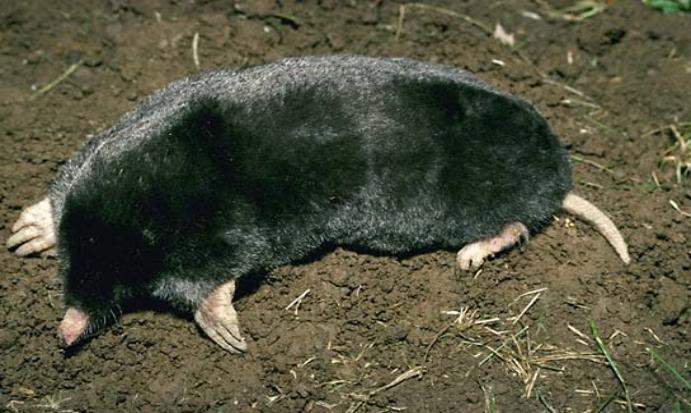

What damage do they do?
Named insectivores, they burrow year round in their subterranean system (regularly utilizing each passage just once) looking for night crawlers, hatchlings (grubs) and different bugs on which they feed. Overseeing moles is not generally fundamental, as they don't eat plants. In any case, their passages can be an issue as they push up hills of earth and regularly hurt the roots of developing plants.
How to get rid of them?
- Trapping: The best and dependable strategy for controlling moles! Traps ought to be set in early spring when passages are first seen, or after the primary fall downpours. Figure out which passages are dynamic before setting traps.
- Eliminate Grubs: In gardens, moles nourish intensely on soil staying bugs, for example, Japanese scarab grubs. The “Spikes of Death” Lawn Aerator Sandals, Milky Spore and additionally gainful nematodes can be utilized to take out these vermin and will, for the most part, lessen burrowing or nourishing action.
- Repellents: Common castor oil anti-agents function admirably to continue tunneling creatures from yards, gardens and other planting regions. Apply when passages or cone molded hills show up in soil from early spring to late fall.
- Barriers: Burrow a trench approximately 6 inches wide and two feet long. Fill it with shake or line it with wire to keep tunneling nuisances from attacking patio nursery ranges.
- Ultrasonic Devices: The Sonic Mole Chaser doesn't play music, yet rather creates an entering underground sonic heartbeat that makes underground rodents insane.
Mosquitos
How to identify them
In the rainy, humid seasons, the female penetrates the skin and infuses salivation, which is in charge of the aggravation that comes later. Blood taken from people or different creatures contaminated with diseased life forms thus taints the mosquito which transmits them to future hosts.
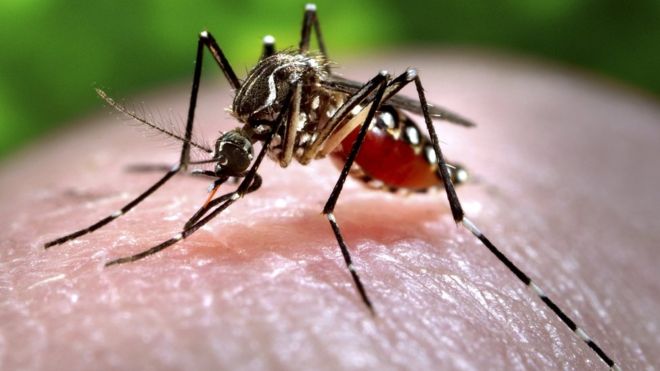
What damage do they do?
They carry some of the most widespread and devastating human disease agents including West Nile virus, encephalitis and malaria. Mosquitoes are also responsible for transmitting heart-worm in dogs. These diseases, infections and illnesses are now found in just about every part of the United States.
How to get rid of them?
Sadly, there is no simple answer for overseeing mosquitoes. Innumerable normal strategies change strategies upon the nuisance level, water supply, cost and danger of illness. Numerous items are accessible, however nothing is completely secure. Here are some proposals:
- Habitat modification
- Reduction in exposure
- Getting rid of larvae before they hatch
- Using environmentally safe pesticides and insecticides for full grown adults
Deer
How does one recognize them?
Deer are basically browsers, so they tend to snack on delicate perpetual plants and young trees.

What damage do they do?
A couple of deer are a tender disturbance; but amid a hard winter, an expansive heard will eat practically everything in sight. One reason that deer are turning into a more serious issue in many parts of the United States is that their numbers are expanding.
How to get rid of them?
Particular strategies for keeping deer away differ according to the neighborhood populace, accessible sustenance supplies, cost, plants' harm resilience and sorts of plants developed. Numerous arrangements are accessible, yet nothing is completely foolproof.
Ticks
How does one recognize them?
Grown-ups (1/4 inch long) have eight legs and are rosy, dark colored with white or yellow unpredictable markings on their body. Females are marginally bigger than guys, and can develop as huge as 1/2 inch long after a drink of blood. To inject, they take hold of a host, discharge a sedative and easily tunnel into the skin with their mouth parts. Bites can cause skin aggravations or even unfavorably susceptible responses in a few people.
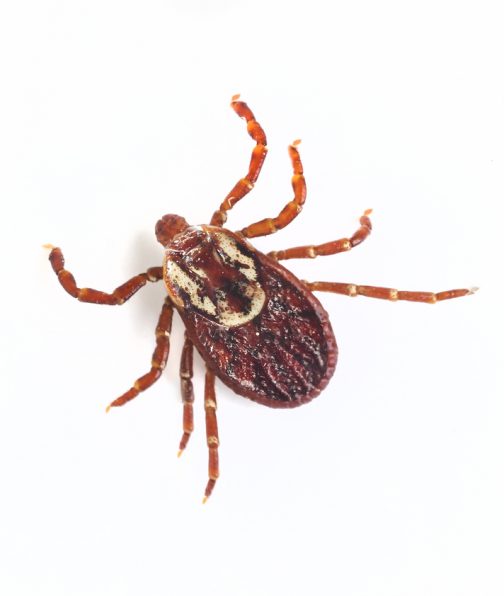

What damage do they do?
Blood sucking other than parasite of vertebrates, winged animals and reptiles, ticks are imperative vectors of illness causing operators. They join solidly to their host, nourish gradually and may go unnoticed for a few days while boosting. Thus, ticks transmit the largest assortment of pathogens of any parasitic arthropod. Some examples of critical human diseases include Lyme illness and Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
How to get rid of them?
- Keep grass and weeds trimmed and evacuate heaps of wood to lessen harborage for ticks.
- At whatever point conceivable, remain out of nuisance invaded ranges, green fields, prairies and lush zones.
- Confine development of your pets.
- When entering plagued territories, wear long-sleeved shirts, and long pants with tight-fitting sleeves.
- Wear light-hued garments. Ticks are less demanding to see on a light foundation.
Hornworm
How does one recognize them?
The tomato hornworm is three to four inches in length at full size (prone to be the greatest caterpillar we find in our greenery enclosures) and green in color, with white V-molded checks along its sides. A dark “horn” ventures from the back of the caterpillar. Tobacco hornworms, then again, have corner to corner white stripes and a red “horn.” Both are dealt with similarly when they assault your garden.
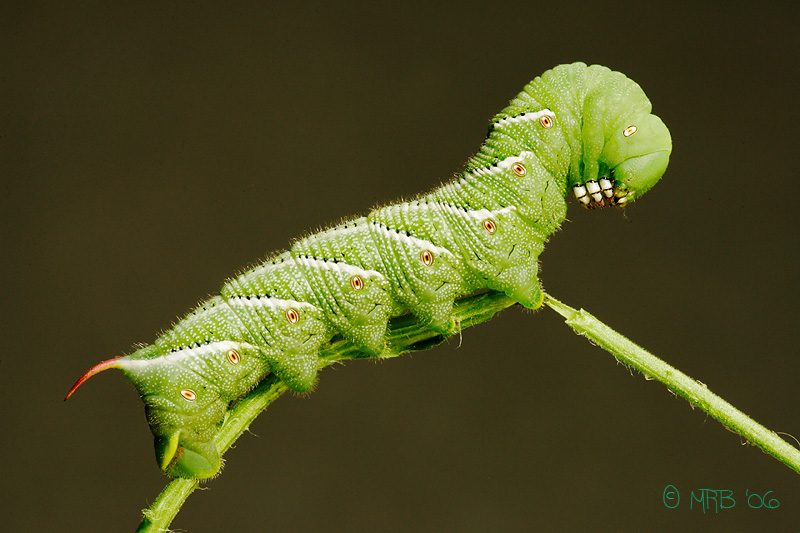

What damage do they do?
Undetected, a tomato hornworm can do a decent lot of harm to its host plant. They have healthy cravings and can defoliate a plant in a matter of days. On the off chance that they are identified and evacuated at an early stage, the plant will recuperate fine and well.
How to get rid of them?
Since the hornworm is so big, the least demanding and best approach to dispose of it is to pick it off of plants when you distinguish it, and either squash it or hurl it into a bowl of foamy water. An awful pervasion can be dealt with by applying BT (Bacillus thuringiensis). This is best when the hatchlings are little. On the off chance that worms are an issue for an endless amount of time, take a stab at rototilling the dirt either in late fall or in spring before you plant- – this will either cover the pupae or pulverize them. The manufactured substance Carbaryl will murder tomato hornworms alongside numerous different vermin. In any case, it is exceptionally lethal and is not preferred for use on edibles.
Wasps
How does one recognize them?
Recognizable proof differs hugely on the species. Most have two sets of wings and a squeezed midriff. They run in hues from dark to metallic greens and blues and change in size from practically minuscule to a few centimeters in length.

What damage do they do?
A few wasps are savage, while others are parasitic. Ruthless wasps murder and devour different bugs and in addition different creatures which they frequently feed to their hatchlings. Parasitic wasps regularly lay their eggs in the collections of living animals like caterpillars or insects. The hatchlings feast upon the living host. A few wasps are forceful species and can sting when undermined.
How to get rid of them?
- The best time to treat is during the evening, when the wasps are less forceful.
- It is basic that the paper envelope of the nest not be torn open amid treatment or the irate wasps will dissipate every which way, causing much more noteworthy issues.
- A full wasp suit fixed at the wrists, lower legs, and neckline is suggested when discarding a nest.
- Treatment of wasps, is best performed around evening time; paper wasps can be dispensed with amid the daytime gave you don't stand specifically beneath the nest amid treatment.
- Most wasp sprays make bugs drop right away when reached by the bug spray.
- Standing specifically beneath a nest builds one's danger of being stung.
- Spraying into a wasp nest ought to ALWAYS be done around evening time. Wasps are far less forceful and are all at home. Alerts ought to be taken while investigating wasps nests amid the day.
Rabbits
How does one recognize them?
Rabbits which are common in the U.S. range from the house cat-sized jackrabbit to their smaller cousins, the cottontails and brush rabbits, which are about 12 inches long. Even if you aren’t able to see a rabbit, you can see clearly that it was there, because rabbits leave behind coarse and circular fecal “pellets” that are about 1/2-inch in diameter.

What damage do they do?
Rabbits prefer to feed on tender young vegetation, but they will also eat seeds, bark, and nuts during their night time feeding cycles. Twigs and flower heads are clipped neatly by the rabbit's incisors, no more than two feet from the ground.
How to get rid of them?
- Fencing
- Tree wrap
- Cleanup
- Rabbit disco
- Repellents
- Trapping
Japanese Beetles
How does one recognize them?
Grown-up creepy crawlies (1/2 inch long) are metallic blue-green with coppery wing covers. They eat blooms and skeletonize the leaves of more than 300 distinctive plant species. Japanese scarabs spend around ten months of the year in the ground as a stout, white grub (3/4 inch long).

What damage do they do?
Grubs eat the foundations of a substantial number of plants. They are particularly damaging to gardens, which will indicate unpredictably molded patches of shriveled, dead or biting the dust grass. Both the grown-up and larval stage (white grubs) are harming and can be an issue in yards, gardens, nurseries, parks, greens, natural product trees, and decorative trees and bushes.
How to get rid of them?
- In the early morning or late night, shake bugs from plants onto ground sheets and crush.
- Put pheromone traps around the border of your property as grown-ups rise (May-July).
- Coasting line cover can be utilized as a physical obstruction to keep grown-up insects from harming plants.
- Spread valuable nematodes on gardens or mulch around plants to slaughter young stages. These tiny, worm-like parasites effectively chase, enter and wreck grubs in the dirt.
- If all else fails, spot treat grown-ups with herbal pesticides. Apply to all leaf surfaces and profound into the plant shelter where creepy crawlies cover up.
Woodpeckers
How does one recognize them?
Woodpeckers generally peck at dead or ailing trees/appendages, yet they have likewise been known to peck at structures, siding, metal as well as aeration and cooling systems. Woodpeckers peck keeping in mind the end goal to discover sustenance, exhume ranges for settling, or make space for nourishment stockpiling. These flying creatures can have a few broods for every year, each with three to six young.

What damage do they do?
Harm caused by woodpeckers in structures can extend from openings in wood to harmed siding and cooling units, making woodpecker administration fundamental.
How to get rid of them?
Woodpecker avoidance depends on physical hindrances and alarm procedures. Physical obstructions made in pecking zones will help dispose of woodpeckers by averting passage. Regularly these are made of steel. Noise scaring procedures are likewise powerful at times. Keep in mind, woodpeckers are protected and any counteractive action or woodpecker control should be consistent with government law.
Conclusion
Albeit regularly viable against home intruders, fake vermin repellants, spray, traps, and toxic substances can be risky if not deadly when inadvertently ingested or touched. Introduction to pesticides can aggravate the skin, eyes, and respiratory framework, upsets hormones, and even causes disease. Family unit chemicals have harming reactions for nature as well. Pesticides can discover their way into groundwater or a stream, lake, or sea and pollute the water hotspots for individuals and creatures. Once in the earth, pesticides can make harm plants and creatures, and in addition clueless people.





No Comments