Green beans are one of the easiest and most popular vegetables to grow. They are extremely hardy and can grow almost anywhere. Beginners and master gardeners alike love growing these fantastic plants. Whether you call them green beans, snap beans or haricot vert, these plants will be an excellent addition to your garden.

Types of Green Bean Plants
There are two types of green beans, pole beans and bush beans. Pole beans grow on a vine and require a trellis or other sturdy structure to support the vines as they climb. Without a support structure the vine intertwines itself along the ground and makes it difficult to harvest the bean pods. Pole beans are generally ready to harvest sixty days (depending on variety) after planting. They produce continuously during the growing season until the first frost.
Bush beans are more compact plants and grow close to the ground. They do not require extra support. Bush beans generally mature more quickly than pole beans. You can grow them in containers or pots because of their compact size. Bush beans are generally ready to pick fifty days (depending on variety) after planting. They produce a large crop over a two week period. If you wish to have green beans available all summer long plant another row of bush beans two weeks after the first. You may continue to do this until ten weeks before the last frost.
Soil and Planting
Green beans are warm weather plants. They grow best in warm soil (above forty-eight degrees Fahrenheit). Plant the seeds in well-drained soil after all danger of frost is past. Bean plants need full sun (six to eight hours) so be sure to pick a sunny place to plant.
Green beans grow best in loamy soil which is soil that is dark and crumbly. If you are unsure of your soil type squeeze a handful of it into a ball. If your soil has a lot of clay it will stay in a ball. If it is sandy it will crumble. If it is loamy it will stay in a ball, but fall apart when touched. Amend your soil with compost if it is heavy clay or sandy the plants for best results. Clay soil does not drain well, and sandy soil lacks essential nutrients. To amend the soil spread two to three inches of compost over the soil and mix it into the top twelve inches. Keep the soil moist as the plants grow. Hot, dry conditions can cause the flowers on the plants to drop off which means no fruit (bean pods) will grow.
The seeds of the bean plants are large and easy to see. Because of the large size they are a great seed for kids to plant. Plant your bush bean seeds six inches apart in rows that are spaced one to two feet apart. Pole beans should be planted eight inches apart. Beans of both varieties should be planted one inch deep. Be sure to keep the plants well-watered. Apply mulch to help the plants retain moisture and to keep the bean pods out of the dirt (which prevents them from rotting).
Support Structures for Pole Beans
After planting the pole bean seeds you will need to install some sort of support structure for the plants to climb on. This does not need to be overly complicated.
Tripod
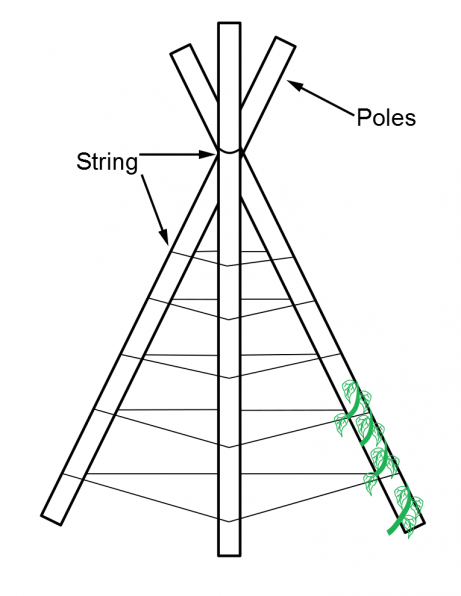
The most popular method of support for pole beans is to construct a tripod. Use poles that are four to six feet tall made from bamboo, PVC, or wood sticks from your yard. Tie three sticks together at one end then spread the legs until the tripod stands on its own. Gently press the legs into the dirt so it won’t fall over. Plant five to six beans and the bottom of each pole. To make the structure sturdier wrap twine or string around the legs in rows six inches apart. As the bean plants begin to grow guide them along the poles and weave them into twine so they stay on the structure and don’t wrap around each other.
Trellis
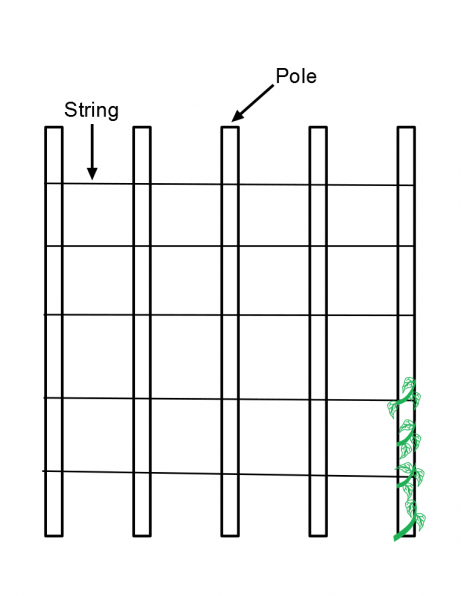
Another option is to install a trellis along a row of beans. This can be something you purchase or make. To make a simple trellis for a row of beans you will need sticks, stakes, or bamboo poles that measure four to six feet in height. Drive the stakes into the ground spaced one foot apart. Tie string to each stake in rows that are spaced twelve inches vertically. Plant three seeds at the base of each pole.
String
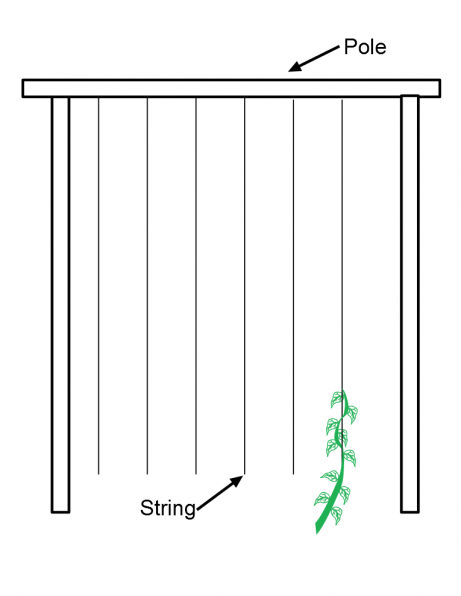
If you are short on poles you can also encourage beans to grow up string that is hanging from a frame. You will also plant your seeds in a row with this method. The length of your poles will determine the length of your rows. If you have six foot bamboo poles then your rows will be six feet long. Place the rows two feet apart. Drive two poles into the ground six feet apart (or the length of your poles). Secure a third pole at the top of the two in the ground. Poles should not be shorter than four feet. Hang string down from the top pole spaced one foot apart. Plant a few seeds below each string. As the plant grows wind the vines around the string to encourage them to grow up string.
Fence
The easiest option for a support structure would be to use a chain-link fence. Plant seeds eight inches apart along the fence. As they grow encourage the vines to grow up the fence by weaving the vines through the chain-links.
Pests and Troubleshooting
Cutworms
Green beans, like all garden plants, are susceptible to a handful of pests. Cutworms can be a problem if the beans are planted in an area that recently grew grass. Cutworms are earth-colored caterpillars that do their dirty work at night. They kill seedlings by grinding the main stem which breaks it. Prevent cutworms by installing a rigid collar on the lowest three inches of the seedling. You can easily make a collar by cutting the top off of a plastic cup. Another option is to wrap foil around the base of the stem. Both options prevent the worms from grinding. Cutworms will no longer be an issue after a couple weeks of growth. At that point the stems are too thick for the worms.
Slugs and Japanese Beetles
Slugs and Japanese beetles enjoy green bean leaves and eat holes through the leaves. Trap slugs in shallow containers filled with beer. Use row covers to prevent Japanese beetles.
Rabbits
One of the biggest pests in your vegetable garden, and will not be restricted to green bean plants, may be rabbits. Rabbits love nibbling on the tender, new growth of plants. Rabbits are very prolific and can produce as many as 18 babies in one season. You will probably never get rid of rabbits completely, but there are methods you can use to deter them from your yard. One method is to spread fox urine granules around your yard. Rabbit are prey to fox and they will not enter an area they think contain foxes. Fox urine may be found at your local garden center. Another method is to spray your plants with a mixture of tabasco and water. Mix one gallon of water with one tablespoon of tabasco and spray on any plants you do not want rabbits eating.
Brown Spots on Leaves
Brown spots on the leaves of the bean plants could be a bacterial disease called brown spot or blight. Brown spot occurs as small brown spots on the leaves encircled by a ring of yellow or light green. Brown spot is spread by the wind with the infection coming from weeds. Humid weather can cause the spots to spread more quickly. Use a copper-based spray to help eliminate the bacteria. Blight also appears as brown spots encircled by yellow rings which spreads until the whole leaf is covered and dies. Blight is spread by inspects and rain. Remove infected leaves before it can spread.
Yellow Leaves
Yellow leaves can be an indication of many different problems. If the plants are not getting enough sun the leaves will not be able to produce enough chlorophyll and may turn yellow. Overwatering may cause the roots to rot which would also cause yellow leaves. Yellow leaves could also be an indication of nutrient deficiency. If this occurs apply nitrogen to the soil. Nitrogen can be added chemically (fertilizer) or organically (coffee grounds or composted manure for example).
When to Harvest Beans
The general rule of thumb when picking green beans is they are ready when they are four to seven inches in length and about the diameter of a pencil. Beans should be harvested every other day. Picking beans promptly encourages the plant to blossom and grow more beans. Use two hands when picking, one on the stem and one to pull the beans. If you pull too hard you may break the tender vine. Extra beans may be preserved by freezing, canning, or drying.








No Comments